Let's delve into the Safety Management Information Module, which maintains connections with numerous other informational and operational modules. Across the civilized world, adherence to a quality standard for work production and service provision, typically embodied by ISO standards, is widespread. While subject to periodic updates and modifications, the core essence remains constant: the presence of relevant rules, conditions, and requirements for diverse production processes. These encompass the development of training and certification programs for specialists and workers, ensuring their qualification for work admission while mitigating risks to life and health.
Based on such programs, various security certificates are formulated, delineating levels of admission and corresponding responsibilities incumbent upon enterprise employees. Workers undergo certification through various organizations accredited at the state level for safety training and certification purposes.
Hence, the primary objective of the Safety Technique Information Module is to uphold operational control and maintain records pertaining to safety within the business, thereby averting incidents and accidents at the enterprise. This endeavor aims to cultivate an image of an exemplary and dependable company in the eyes of both customers and clients.
In scenarios where a company engages multiple suppliers and subcontractors, a system becomes imperative for tracking their certificates and licenses for the services rendered. This facilitates swift evaluations of these entities' adherence to service quality standards and safety protocols. As observed, the company selects the most suitable supplier based on the safety performance indicators of the contracted entity.
Interconnectedness permeates this framework: by ensuring safe working conditions and minimizing production incidents, not only does the quality of products and services improve, but the company also gains stature in the eyes of prospective customers.
-
Safety Certificates Table: This table will list the safety certificates pertinent to your business and mandatory for employees.
-
Training and Certification Providers Table: This table will enumerate the companies offering training and certification programs for personnel.
-
Employee Certificates Link Table: This table will serve as a link between company employees and their respective certificates, establishing associations between them.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Management Table: This table will facilitate the management of personal protective equipment, potentially functioning as a virtual warehouse for safety gear.
-
Assigned Equipment Table: This table will manage the equipment allocated to individual workers, including items such as working clothes, ensuring efficient tracking and maintenance.
These tables form the foundation for a comprehensive safety management database, enabling efficient management of certificates, training programs, protective equipment, and associated resources essential for ensuring workplace safety.
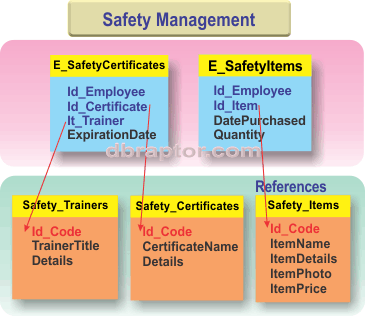
Diagram of Safety Management module
Indeed, as evident, there's no need for complex technology to establish a robust system for managing safety measures. By creating a user-friendly interface to handle this straightforward data, strict and effective accounting for safety measures can be readily achieved. Such responsibilities can be efficiently overseen by an administrative officer empowered to monitor database notifications regarding impending expiration of employee certificates and facilitate enrollment in certificate renewal courses. Essentially, in a relatively well-functioning company, the necessity for a highly educated and consequently expensive safety specialist may not arise.
However, if management begins to receive signals indicating safety regulation violations, incident reports accumulate, and product sales decline, these are clear indicators of negative trends. In such instances, it becomes imperative to take proactive measures to prevent further incidents within the enterprise. This entails establishing an additional table to record incident dates, participant details, incident types, and quantitative risk assessments. Subsequently, analyzing these records becomes essential. Naturally, for in-depth and thorough analysis, the expertise of a safety specialist is indispensable. A competent expert can significantly assist management in steering the company away from negative trends and towards improved safety practices.




You need to be registered for ability to comment articles.